
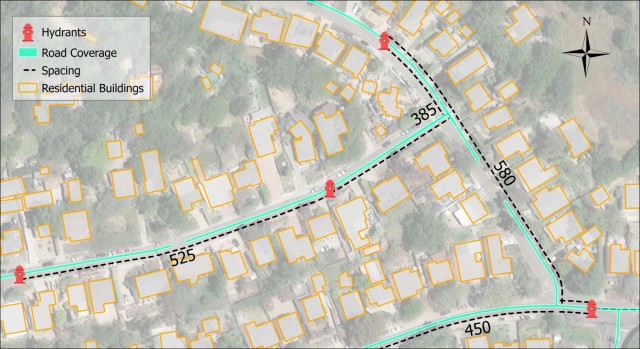
Hydrant Access & Fire Code Compliance
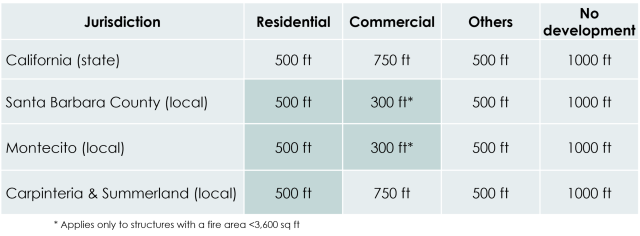
Firefighters need reliable access to water when responding to fire emergencies, making the placement of fire hydrants extremely critical. In California, there are specific standards for hydrant spacing in order to ensure suitable access: 500 ft for residential areas, 750 ft for commercial zones, and 1000 ft for undeveloped regions. These standards are designed to protect life and property during an incident. Effective fire response depends on the spatial distribution of hydrants and associated access. WRI researchers investigated hydrant spacing in Santa Barbara to evaluate fire safety compliance of properties, streets, neighborhoods and areas.
California Fire Code (2022)
- CFC Section C103 - Average spacing between hydrant (with conditions): 500 ft (max distance to street frontage: 250 ft)
- C103.1 Hydrant Spacing - Fire apparatus access roads and public streets providing required access to buildings in accordance with Section 503 shall be provided with one or more fire hydrants, as determined by Section C102.1."
SBC Fire Department (2023)
- Development Standard #2 - Urban and Rural Development (Non-sprinklered): 500 ft spacing / 1000 gpm flow rate
- 5.1 HYDRANT SPACING. Hydrant spacing shall be determined and maintained in accordance with this section. Spacing is based on the distance between hydrants along an approved access road. Specific locations shall be approved by the Fire District prior to project approval.
Evaluation Based on Spatial Data Science
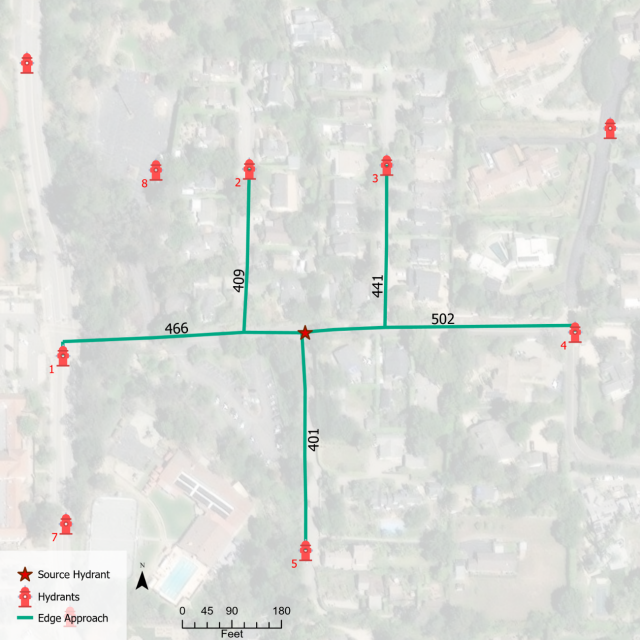
The assessment of hydrant spacing was based on spatial data science. GIS (geographic information systems) and spatial analytics were used to derive spacing in Santa Barbara. Based on observed spacing, evaluation of fire safety compliance of hydrant spacing standards was possible at any geographic scale.
The assessment of hydrant spacing was based on spatial data science. GIS (geographic information systems) and spatial analytics were used to derive spacing in Santa Barbara. Based on observed spacing, evaluation of fire safety compliance of hydrant spacing standards was possible at any geographic scale. This identification consisted of finding the neighbors for each hydrant by exploring traversable road paths based on two rules:
- hydrant neighbor only if it can be accessed via the shortest path
- path must not contain any other hydrants
Road centerline information, land use and hydrant locations were the starting point. As an example, the figure above shows the following set of identified neighbors using this criteria: N0={1,2,3,4,5}. Based on the identified paths, distances can be derived and assessment undertaken with respect to 2022 California Fire Code.
Practical Implications
The study found that much of the region has hydrant spacing that is within stipulated fire safety standards, but significant spacing gaps were identified throughout Santa Barbara. Residential areas require hydrant spacing to be no more than 500 ft. With an average spacing of 561 ft, 52% of residential areas satisfy the fire safety standard. 92% of commercial areas have hydrant spacing within the 750 ft standard. In undeveloped areas of the region some 52% are within the 1000 ft spacing standard.
Excessive hydrant spacing make timely access more difficult, making advanced planning for emergency response efforts essential.
What is the hydrant spacing in your neighborhood? An interactive WRI portal/website allows you to examine any area of the region.
References
Figueroa, V. E., Murray, A. T., & Funk, T. (2024). Supporting Fire Response: Advanced Spatial Data Analytics for Hydrant Access Assessment. Transactions in GIS, 28(8), 2559-2573.
Contacts

